
What is Browser Isolation?

Background of Browser Isolation
Web browsers are one of the most common business applications used today. Organizations of every size in every industry rely on the internet one way or the other to successfully conduct their business. Unfortunately, web browsers also present a huge security liability as a major access point for malware to infiltrate business machines.
Traditionally, organizations have relied on a wide range of security solutions for web-based malware protection. Some solutions use an algorithm to determine if the web content coming into a network is good or bad. Other solutions block users from navigating to websites that might contain dangerous code. Examples of these kinds of security products include web proxies and secure web gateways.
While effective, these approaches may miss zero-day malware, and blocking users from websites can have a negative effect on productivity. Cybersecurity industry statistics and trends continue to show that security spending is high and still rising as organizations struggle to provide adequate security measures against malware.
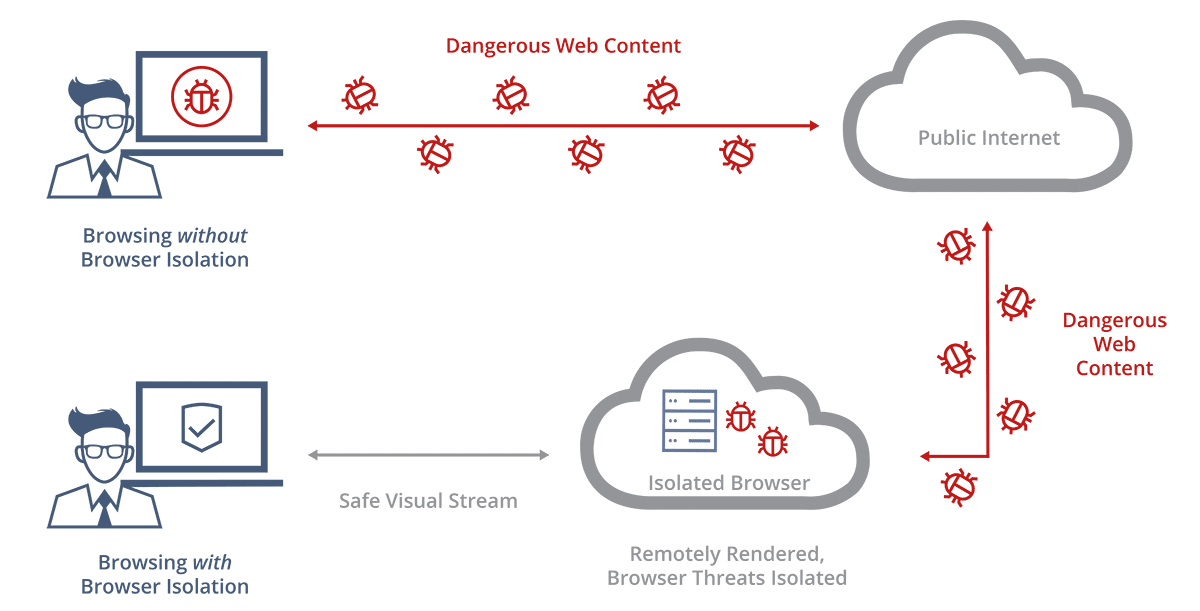
In response to these issues, the concept of Browser Isolation was the result of thinking through what it would take to completely stop web-based malware from infiltrating a network. Instead of trying to keep users away from unsafe websites, isolated browsing allows users to safely access any website, even if it is malicious. Browser Isolation technology adopts a Zero Trust approach in assuming no web content is safe. All user browsing activity is moved to an isolated environment away from the user’s computer. Since no web content actually ever reaches the user’s computer, malware has no entry point into the system.
What’s the difference between Browser Isolation and Remote Browser Isolation?
Remote Browser Isolation is a specific implementation of Browser Isolation that occurs remotely by moving the execution of all browsing activity from the user’s computer to a remote server. This remote server can be hosted in the cloud or located on-premise within an organization’s network.
However, in the cybersecurity industry, when someone says Browser Isolation they often really mean Remote Browser Isolation.
The benefit of performing the isolation remotely is that it offers greater security and requires lower client-side resources as compared to performing the isolation locally on the user’s computer.
How does Browser Isolation Technology work?
There are different implementation details that vary amongst Browser Isolation vendors but generally, Browser Isolation works by:
-
- Removing browsing activity from a user’s computer and executing it in a virtual environment.
- Automatically destroying the browsing environment at the end of every browsing session, so if the user ever comes across anything malicious, it gets wiped away at the end of the session. When the user connects to the secure virtual browser again, he/she gets a clean, new image free of any malware. While this isn’t a requirement for Browser Isolation to work, it’s likely a common feature in various solutions.
You can think of Browser Isolation as the difference between a fighter pilot and a drone pilot. A drone pilot can accomplish just about anything an actual fighter pilot can accomplish, but without ever going into the war zone and putting the pilot’s life in danger.
Using Browser Isolation is like being a drone pilot. You can browse the web from a remote location, keeping your network out of harm’s way, but it’ll feel like you’re right there in the middle of the action.
Types of Isolated Browsing
There are two main types of isolation technology: local isolation and remote isolation.
Local Isolation
Most people are aware of local isolation, which is the traditional way isolation was done. It involves using either a sandbox or a virtual machine on the user’s local computer to isolate the data on their computers from dangerous web browsing.
Remote Isolation
With Remote Browser Isolation, the virtualization and isolation happen on a remote server. The user’s browsing activity is moved to a remote virtual environment, and only a real-time visual stream of what is happening on the server is sent to the user’s computer. The remote server can be located on-premise within an organization’s network or hosted in the cloud.
Within the Remote Browser Isolation space, there are degrees to which a particular technology isolates the user’s computer from web content:
-
- DOM Mirroring filters out certain types of web content that it considers dangerous, but still allows some types of web content from the internet directly to the user’s computer in its original form. It is not true isolation.
- Isolation does not send any web content to the user’s computer. It sends only a visual stream in the form of pixels.
Reasons your organization needs Isolated Browsing
Contrary to popular belief, organizations of any size can be seriously impacted by web-based malware, here’s why:
Web Browsing Is Dangerous
Web browsers are the most common business application used today and are inherently difficult to secure because of their complexity. They carry out the most dangerous action a computer program can perform, which is to download untrusted code and execute it directly on a user’s computer. It is no wonder that browser-based attacks are the primary threat vector for attackers to target users.
Blocking Sites Impacts Productivity
Remote Browser Isolation complements a secure web gateway by enabling safe access to websites that are not yet categorized by the secure web gateway. Organizations typically block access to uncategorized websites in an attempt to protect the network from web-based malware. However, the practice of aggressively blocking access to websites results in a decrease in productivity for both end users and the IT team tasked with following up on end user requests to unblock websites. Remote Browser Isolation allows users – and IT teams – to be more productive by using the web as they usually would, without negatively impacting or slowing their user experience – all the while remaining fully protected from web-based threats.
Users are an Enormous Risk
Most users are not careful and can easily be tricked into clicking a malicious link through social engineering tactics. Organizations allocate significant budget resources to perimeter defenses, but one careless employee can circumvent it all by clicking one bad link and opening the front door for an attacker.
Benefits of Web Isolation Technology
Isolated browsing ensures no malicious web content ever reaches the corporate network by isolating all browsing activity in a remote virtual environment. Web Isolation technology protects against all web-based threats.
The key benefits of this approach are:
- Protection From Malicious Websites:
Because no local code execution happens on the user’s computer, users are protected from all malicious websites. - Protection From Malicious Links:
Since URLs are automatically opened in the isolated web browser, whether they’re in webpages, emails, documents, Skype, etc., users are protected regardless of the source. - Protection From Malicious Emails:
With Web Isolation, all web-based emails are rendered harmlessly in the remote server, and links in email clients are automatically opened in the remote server as well. - Protection From Malicious Downloads:
Administrators can finely control which files users are permitted to download, and all permitted downloads are first scanned to eliminate threats. - Protection From Malicious Ads:
Ads and trackers are automatically blocked. If any ads are displayed, they’re rendered remotely – protecting the user from malicious content. - Anonymous Browsing:
Advanced anonymous browsing capabilities mask users’ true identities. - Data Loss Prevention:
Built-in DLP capabilities protect corporate data from being accidentally or intentionally exfiltrated. These capabilities allow an administrator to restrict the files a user can upload to the internet. - User Behavior Analytics:
Organizations can obtain analytics into users’ web activities, which can be used for compliance monitoring, and to detect insider threats and unproductive employees. - Reduced Number of Security Alerts:
Isolating all web content on a remote server results in fewer security alerts and false positives that need to be investigated. - Eliminates the Cost of Web-Based Malware:
The effects of a malware infection can be severe and require a substantial amount of money and time to fix. Isolated browsing protects your network completely from web-based malware.